Motion - NCERT Questions
An object has moved through a distance. Can it have zero displacement? If yes support your answer with an example.
SOLUTION:Yes, the object instead of moving through a distance can have zero displacement. Example: If an object travels from point A and reaches to the same point A, then its displacement is zero.
Q 2.A farmer moves along the boundary of a square field of side 10 m in 40 s. What will be the magnitude of displacement of the farmer at the end of 2 minutes 20 seconds?
SOLUTION: 
Which of the following is true for displacement? (A) It cannot be zero. (B) Its magnitude is greater than the distance travelled by the object.
SOLUTION:A. False.
B. False
Distinguish between speed and velocity?
SOLUTION: 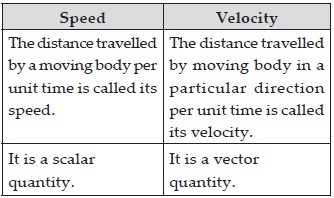
Under what condition(s) is the magnitude of average velocity of an object equal to its average speed?
SOLUTION:The magnitude of average velocity of an object is equal to its average speed if the object moves in a straight line in a particular direction.
Q 6.What does the odometer of an automobile measure?
SOLUTION:The odometer of an automobile measures the distance travelled by a vehicle.
Q 7.What does the path of an object look like when it is in uniform motion?
SOLUTION:It is a straight line.
Q 8.During an experiment, a signal from a spaceship reached the ground station in five minutes. What was the distance of the spaceship from the ground station? The signal travels at the speed of light, that is 3 × 108 m s–1?
SOLUTION: 
When will you say a body is in (i) uniform acceleration (ii) non-uniform acceleration
SOLUTION:(i) Uniform acceleration : When a body
travels with the same velocity in the
given time, then the acceleration is said
to be uniform.
(ii) Non-uniform acceleration : When a
body moves with unequal velocity in
the equal interval of time, the body is
said to be moving with non-uniform
acceleration.
A bus decreases its speed from 80 km h–1 to 60 km h–1 in 5 s. Find the acceleration of the bus.
SOLUTION: 
A racing car has a uniform acceleration of 4 m s–2. What distance will it cover in 10 s after start?
SOLUTION: 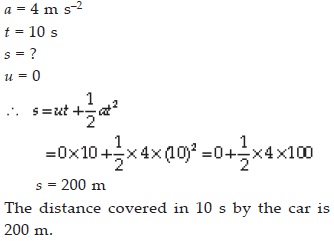
A stone is thrown in a vertically upward direction with a velocity of 5 m s–1. If the acceleration of the stone during its motion is 10 m s–2 in the downward direction, what will be the height attained by the stone and how much time will it take to reach there?
SOLUTION: 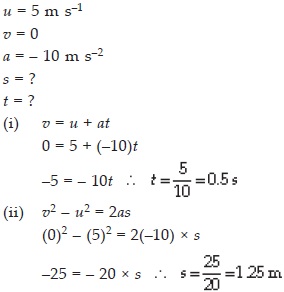
An athelete completes one round of a circular track of diameter 200 m in 40 s. What will be the distance covered and the displacement at the end of 2 minutes 20 s?
SOLUTION: 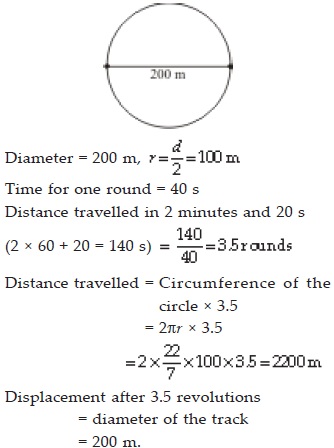
Joseph jogs from one end A to the other
end B of a straight 300 m road in 2 minutes
30 seconds and then turns around and jogs
100 m back to point C in another 1 minute.
What are Joseph’s average speeds and
velocities in jogging. (A) from A to B and
(B) from A to C?

Abdul, while driving to school, computes the average speed for his trip to be 20 km h–1. On his return trip along the same route, there is less traffic and the average speed is 30 km h–1. What is the average speed for Abdul’s trip?
SOLUTION: 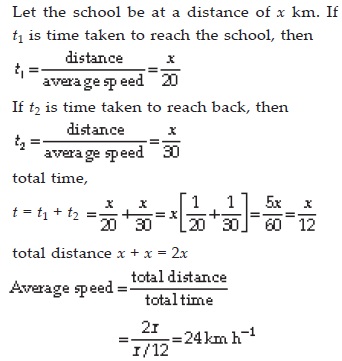
A motorboat starting from rest on a lake accelerates in a straight line at a constant rate of 3.0 m s–2 for 8.0 s. How far does the boat travel during this time?
SOLUTION: 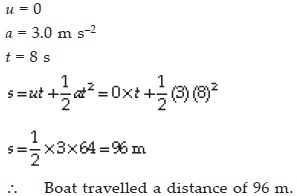
A driver of a car travelling at 52 km h–1 applies the brakes and accelerates uniformly in the opposite direction. The car stops in 5 s. Another driver going at 3 km h–1 in another car applies his brakes slowly and stops in 10 s. On the same graph paper plot the speed versus time graphs for the two cars. Which of the two cars travelled farther after the brakes were applied?
SOLUTION: 
Figure given below shows the distancetime
graph of three objects A, B and C,
study the graph and answer the following
questions?
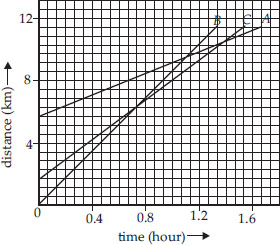
(A) Which of the three is travelling the
fastest?
(B) Are all three ever at the same point on
the road?
(C) How far has C travelled when B passes
A?
(D) How far has B travelled by the time it
passes C?
(A) B is travelling fastest.
(B) As three lines do not meet at any point,
the three objects never meet on the
road.
(C) B passes A at D. At this time, C is at E,
which corresponds to 7 km. Hence when
B crosses A, then C is at 7 km from the
origin.
(D) By the time B passes C, it has travelled
4.5 km.
A ball is gently dropped from a height of 20 m. If its velocity increases uniformly at the rate of 10 m s–2, with what velocity will it strike the ground? After what time will it strike the ground?
SOLUTION: 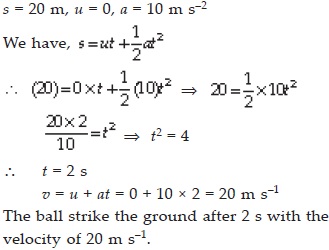
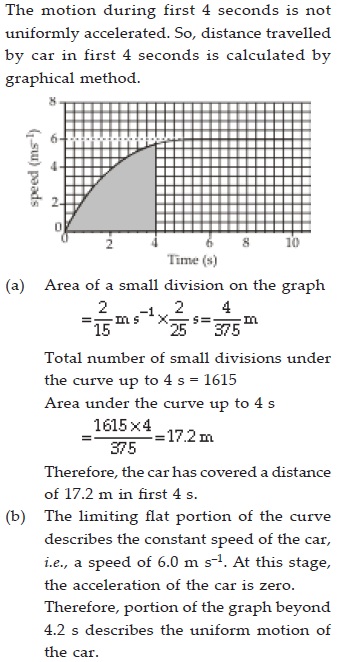
The speed-time graph for a car is shown in
the figure.
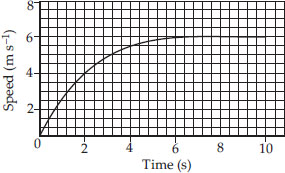
(A) Find how far does the car travel in the
first 4 seconds. Shade the area on the
graph that represents the distance
travelled by the car during the
period.
(B) Which part of the graph represents
uniform motion of the car?
State which of the following situations are possible and give an example for each of
these :
(A) an object with a constant acceleration
but with zero velocity
(B) an object moving in a certain direction
with an acceleration in the perpendicular
direction
(A) free fall due to gravity
(B) object moving in a circular path
An artificial satellite is moving in a circular orbit of radius 42250 km. Calculate its speed if it takes 24 hours to revolve around the earth.
SOLUTION: 