Civics - Class 8
Social and Political Life - III
Chapter 5: Judiciary
Intext Questions:
Question 1:
Answer :
- Controversy of Tehri Dam at Uttarakhand. Implementation of VAT on various products throughout the country was not accepted by the most states. Thus, it became a matter of controversy.
- Distribution of water of river Godavari between Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh.
- Forcible construction or extend¬ing wall on the neighbour’s plot.
- Refusing to admit a badly injured person in the govern¬ment hospital means devoiding the person from his right to life which is mentioned in our Constitution.
Question 2: Do you think that any ordinary citizen stands a chance against a politician in this kind of judicial system? Why not?
Answer :
Any ordinary citizen cannot stand against a politician where the politician has the power to appoint and dismiss a judge from his office. Because the control that the politician holds over the judge does not allow for the judge to take an independent decision. The lack of independence would force the judge to make judgments in favour of the politician.
Question 3: List two reasons why you believe an independent judiciary is essential to democracy.
Answer :
- It allows the courts to play a crucial role in ensuring that there is no misuse of power by the legislature and the executive.
- It will also help in protecting the Fundamental Rights of citizens because anyone can approach the courts if they believe that their rights have been violated.
Question 4: The structure of the courts from the lower to the highest level is such that it resembles a pyramid. Having read the description above, can you fill out which type of courts would exist at what level in the following diagram?
Answer :
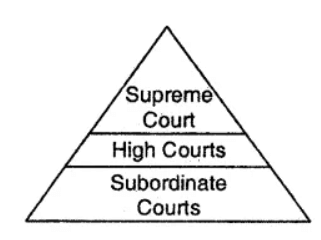
Question 5: Write two sentences of what you understand about the appellate system from the given case.
Answer :
In the appellate system, if a person believes that the judgment passed by the lower court is not just he/she can appeal to a higher court.
Question 6: Fill in the table given below based on what you have understood about criminal and civil law.
Answer :
Question 7: Discuss the impact of the shortage of judges on the delivery of justice to the litigants
Answer : When there is shortage of judges then there is denial or delaying in providing justice to the litigants. There are many cases pending and due to shortage of judges timely justice could not be provided. Hence, shortage of justice is a drawback in the Indian judicial system.
Exercises
Question 1: You read that one of the main functions of the judiciary is 'upholding the law and Enforcing Fundamental Rights'. Why do you think an independent judiciary is necessary to carry out this important function?
Answer :The independence of the judiciary allows the courts to play a central role in ‘upholding the law and Enforcing Fundamental Rights’ as it ensures that there is no misuse of power by the legislature and the executive. Anyone can approach the courts if they believe that their rights have been violated and Politicians or other socially powerful people cannot use their power to change any judgement.
Question 2: Re-read the list of Fundamental Rights provided in chapter 1. How do you think the Right to Constitutional Remedies connects to the idea of judicial review?
Answer :The Right to Constitutional Remedies allows an Indian citizen to move the court if he feels that any of his or her Fundamental Rights has been violated by the State. As thefinal interpreter of the Constitution, the judiciary has the power to review or even strike down any particular law passed by the Parliament if it believes that this law violates the basic structure of the constitution, which is called judicial review. In this way we find that the Right to Constitutional Remedies given in the Fundamental Rights is directly connected and supported by the idea of judicial review.
Question 3: In the following illustration, fill in each tier with the judgments given by the various courts in the Sudha Goel case. Check your responses with others in class.
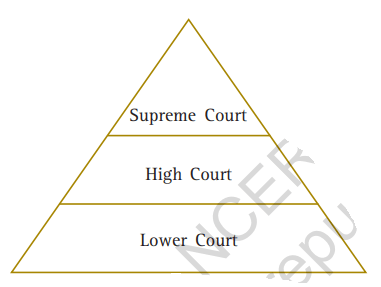
Answer :
Lower Court (Trial Court): Laxman, his mother Shakuntala and his brother-in-law Subhash Chandra were sentenced to death
High Court: Laxman, Shakuntala and Subhash Chandra were acquitted.
Supreme Court: Laxman, Shakuntala were given life imprisonment while Subhash Chandra was acquitted for lack of sufficient evidence.
Question 4: Keeping the Sudha Goel case in mind, tick the sentences that are true and correct the ones that are false.
(a) The accused took the case to the High Court because they were unhappy with the decision of the Trial Court.
(b) They went to the High Court after the supreme Court had given its decision.
(c) If they do not like the Supreme Court verdict, the accused can go back again to the Trial Court.
Answer :
(a) True
(b) False, They went to the High Court after the Trial Court had given its decision.
(c) False, If they do not like the Supreme Court verdict, the accused cannot go back again to the Trial Court since the Supreme Court is at the highest rung of the judiciary pyramid.
Question 5: Why do you think the introduction of Public interest Litigation (PIL) in the 1980s is a significant step in ensuring access to justice for all?
Answer :The introduction of Public Interest Litigation (PIL) in the 1980s is a significant step in ensuring access to justice for all because it also keeps in mind the interests of the illiterate and poor who are not educated enough or cannot afford to access the Indian legal system for justice against exploitation or violation of their basic human and Fundamental Rights.
Question 6: Re-read excerpts from the judgment on the Olga Tellis vs Bombay Municipal Corporation case. Now write in your own words what the judges meant when they said that the Right to Livelihood was part of the Right to Life.
Answer :In Olga Tellis vs. Bombay Municipal Corporation case, the judges said that the Right to Livelihood was part of the Right to Life. They stated that life does not merely imply an animal existence; it cannot be lived without a means of living, that is, "the means of livelihood".
The judges conferred that eviction from a pavement or slum is deprivation of means of livelihood for the poor who cannot afford to live anywhere else. They take up small jobs in surrounding areas and to lose their pavement or slum would lead to loss of a job resulting in loss of a means of livelihood. Consequently, leading to "deprivation of life". This is how the judges connected Right to Livelihood to the Right to Life.
Question 7: Write a story around the theme, ‘Justice delayed is justice denied’.
Answer :
Mohan was the only bread earner of his family. He was killed in an accident, leaving behind his widow and two daughters in 1980. His widow filed a case for compensation and a job on compassionate ground. The court lingered on the case for more than 28 years. She worked on the fields and her daughters worked as domestic help.
With hard work, she was able to earn her livelihood. She borrowed money from the landlord and got her daughters married to poor grooms. The case was decided and compensation of 5 lakhs was awarded to her. Now this money does not have any value for the widow. Justice has been delayed for 28 years. Hence, it is rightly said that justice delayed is justice denied.
Question 8: Make sentences with each of the glossary words given on Textbook Page No. 65.
Answer :
- Acquit – Neha was acquitted of theft charges against her.
- To Appeal – Ramesh appealed against the lower court’s decision in a higher court.
- Compensation – Shobha was given compensation against the neighbour’s harassment.
- Eviction – Ashok’s house was evicted and was given to the owner by the court.
- Violation – Mohan Singh was punished because he forced a man to keep in his house and thus there was a violation of one’s Fundamental Rights.
Question 9: The following is a poster made by the Right to Food campaign.
Read this poster and list the duties of the government to uphold the Right to Food.
How does the phrase “Hungry stomachs, overflowing godowns. We will not accept it!!” used in the poster relate to the photo essay on the Right to Food on page 61?

Answer :
The duties of the government:
- To see that no one goes hungry.
- To provide food to all.
- To see that no one dies of hunger.
- To watch that everyone has balanced food.
This phrase relates to the photo essay on the Right to Food on page 65 because
- People in Rajasthan did not have sufficient food during the drought.
- But the government godowns and those of Hoarders and Black-marketers were full of grains.
- This situation was not acceptable to the people.