Geography - Class 6
The Earth: Our Habitat
Chapter 6: Major Landforms of the Earth
Question 1. Answer the following questions briefly.
- What are the major landforms?
Answer: The major landforms are:-
- Mountains
- Plateaus
- Plains
- What is the difference between a mountain and a plateau?
Answer:
Mountain Plateau Mountain is the natural elevation of the Earth's surface. Plateau is an elevated flat land. The mountains may have a small summit and broad base. It is a flat-topped tableland, standing above the surrounding area. - What are the different types of mountains?
Answer: There are three different types of mountains:- Fold mountains, Block mountains, and Volcanic mountains.
Fold mountains:
- Fold mountains are created where two or more of Earth's tectonic plates are pushed together.
- Examples are the Aravali range, the Himalayas.
Block mountains:
- These are created when large areas are broken and displaced vertically.
- Examples are the Rhine valley and the Vasges mountains in Europe.
Volcanic mountains:
- These are formed due to volcanic activity.
- Examples are Mount Kilimanjaro in Africa and Mount Fujiyama in Japan.
- How are mountains useful to man?
Answer: Mountains are very useful for us because,
- they are a storehouse of water.
- Water from the mountains is also used for irrigation and the generation of hydroelectricity.
- Mountains have a rich variety of flora and fauna.
- Several sports like paragliding, hang gliding, river rafting, and skiing are popular in the mountains.
- Mountains promote tourism.
- How are plains formed?
Answer: The plains are formed by the rivers and their tributaries. The rivers flow down the slopes of mountains and erode them. They carry forward the eroded material and then deposit stones, sand, and silt along with their courses and in their valleys. These deposits form the plains.
- Why are the river plains thickly populated?
Answer: The river plains are thickly populated because the plains are very fertile so the construction of a transport network is easy on them.
- Why are mountains thinly populated?
Answer: The mountains are thinly populated because:-
- It has a harsh climate.
- The slopes are steep here, so less land is available for farming.
Question 2. Tick the correct answer.
- The mountains differ from the hills in terms of
- elevation
- slope
- aspect
- Glaciers are found in
- the mountains
- the plains
- the plateaus
- The Deccan Plateau is located in
- Kenya
- Australia
- India
- The river Yangtze flows in
- South America
- Australia
- China
- An important mountain range of Europe is
- the Andes
- the Alps
- the Rockies
Answer:
- (i) elevation
- (i) the mountains
- (iii) India
- (iii) China
- (ii) the Alps
Question 3. Fill in the blanks.
- A ___________ is an unbroken flat or a low-level land.
- The Himalayas and the Alps are examples of _______________types of mountains.
- _____________ areas are rich in mineral deposits.
- The _________________ is a line of mountains.
- The ____________areas are most productive for farming.
Answer:
- A plain is an unbroken flat or a low level land.
- The Himalayas and the Alps are examples of fold types of mountains.
- Plateau areas are rich in mineral deposits.
- The range is a line of mountains.
- The plain areas are most productive for farming.
Map Skills
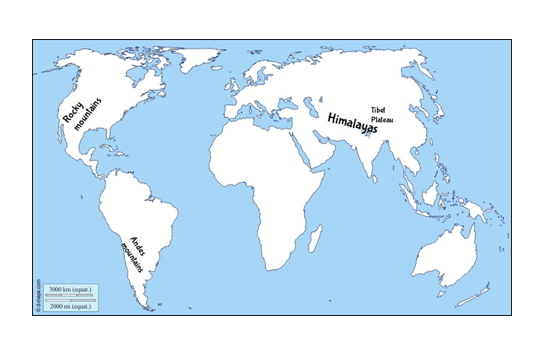
Question: On an outline map of the world, mark the following :
- Mountain ranges: Himalayas, Rockies and Andes.
- Plateau : Tibet.
Answer:
-
Himalayas: mountain range is in South and East Asia separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau.
Rockies: lies in North America and stretches in the northernmost part of western Canada, to New Mexico in southwestern United States.
Andes: The Andes extends through seven South American countries: Venezuela, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia, Chile, and Argentina. - Tibetan Plateau: The region lies between the Kunlun Mountains and its associated ranges to the north and the Himalayas and Karakoram Range to the south and southwest, respectively; it extends eastward to the Daxue Mountains and, farther south, the northern and central portions of the Hengduan Mountains.
Activity:
Question:


Answer:
- Photograph no.1- Camel riding and the struggle of drinking water in the desert region.
- Photograph no.2- Coastal plain(Beach).
- Photograph no.3- Boat racing on the river.
- Photograph no.4- Sea-side trees and huts.
- Photograph no.5- Houses in the mountainous region.
- Photograph no.6- Cultivation of tea on the mountains.
- Photograph no.7- Terrace farming in the hilly regions.
- Photograph no.8- An adventure sport-River rafting.
- Photograph no.9- Cattles grazing on the mountains.
- Photograph no.10- Snowfall on the roads.
- Photograph no.1- Desert region.
- Photograph no.2- Coastal region.
- Photograph no.7- Mountainous region.
- Cattle grazing
- Photograph no.3- Boat racing.
- Photograph no.6- Tea cultivation.
- Photograph no.8- River rafting.
- Photograph no.9- Cattles grazing on the mountains.
- Photograph no.4- Huts.
- Photograph no.5- Houses in the mountainous region.
- Photograph no.3- Boat racing.
- Photograph no.8- River rafting.
- Photograph no.1- Camels.
- Photograph no.10- Vehicles.