Basic Geometrical Ideas (Mathematics) Class 6 - NCERT Questions
Use the figure to name :
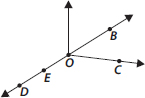
(A) Five points
(B) A line
(C) Four rays
(D) Five line segments
(A) Five points : O, B, C, D, E
(B) A line : 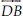
(C) Four rays : 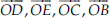
(D) Five line segments : 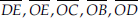
Name the line given in all possible (twelve) ways, choosing only two letters at a time from the four given.

Possible lines are 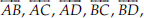
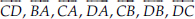
Use the figure to name :
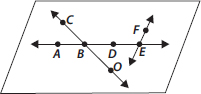
(A) Line containing point E.
(B) Line passing through A.
(C) Line on which O lies.
(D) Two pairs of intersecting lines.
(A) A line containing point 
(B) A line passing through 
(C) A line on which O lies is 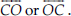
(D) Two pairs of intersecting lines are
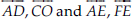
How many lines can pass through
(A) one given point?
(B) two given points?
(A) Infinite number of lines can pass through one given point.
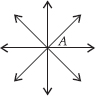
(B) Only one line can pass through two given points.

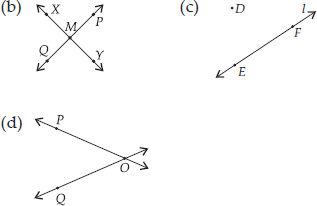
Draw a rough figure and label suitably in each of the following cases:
(A) Point P lies on 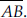
(B) 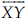 and
and 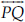 intersect at M.
intersect at M.
(C) Line l contains E and F but not D.
(D) 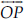 and
and 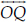 meet at O.
meet at O.
(A) 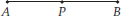
Consider the following figure of line  . Say whether following statements are true or false in context of the given figure.
. Say whether following statements are true or false in context of the given figure.
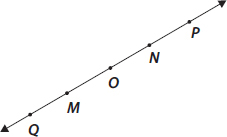
(A) Q, M, O, N, P are points on the line 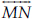 .
.
(B) M, O, N are points on a line segment 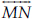 .
.
(C) M and N are end points of line segment 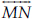 .
.
(D) O and N are end points of line segment 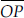 .
.
(E) M is one of the end points of line segment 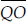 .
.
(F) M is point on ray 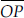 .
.
(G) Ray 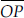 is different from ray
is different from ray 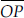 .
.
(H) Ray 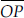 is same as ray
is same as ray 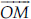 .
.
(I) Ray 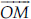 is not opposite to ray
is not opposite to ray 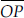 .
.
(J) O is not an initial point of 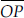 .
.
(K) N is the initial point of 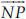 and
and 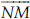
(A) True (B) True (C) True (D) False (E) False (F) False (G) True (H) False (I) False (J) False (K) True
Q 7.Classify the following curves as (I) Open or (ii) Closed.
(A) Open curve
(B) Closed curve
(C) Open curve
(D) Closed curve
(E) Closed curve
Draw rough diagrams to illustrate the following:
(A) Open curve
(B) Closed curve.
(A) Open curves :

(B) Closed curves :
Draw any polygon and shade its interior.
SOLUTION: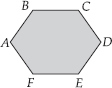
ABCDEF is the required polygon.
Consider the given figure and answer  the questions :
the questions :
(A) Is it a curve?
(B) Is it closed?
(A) Yes, it is a curve.
(B) Yes, it is closed.
Illustrate, if possible, each one of the following with a rough diagram:
(A) A closed curve that is not a polygon.
(B) An open curve made up entirely of line segments.
(C) A polygon with two sides.
(A)  (B)
(B) 
(C) Polygon with two sides cannot be drawn.
Name the angles in the given figure.
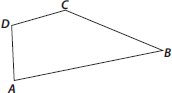
There are four angles in the given figure i.e., ∠ABC, ∠CDA, ∠DAB, ∠DCB
Q 13.In the given diagram, name the point(s)
(A) In the interior of ∠DOE
(B) In the exterior of ∠EOF
(C) On ∠EOF
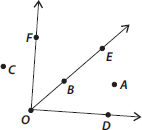
(A) Point in the interior of ∠DOE : A
(B) Points in the exterior of ∠EOF : C, A, D
(C) Points on ∠EOF : E, O, B, F
Draw rough diagrams of two angles such that they have
(A) One point in common.
(B) Two points in common.
(C) Three points in common.
(D) Four points in common.
(E) One ray in common.
(A) 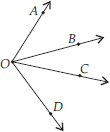
Here, two angles are ∠AOD and ∠BOC and point O is common.
(B) 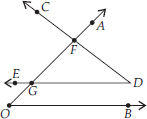
Here, two angles are ∠AOB and ∠CDE and two points F and G are common.
(C) 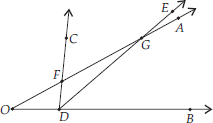
Here, two angles are ∠AOB and ∠CDE and three points F, D and G are common.
(D) 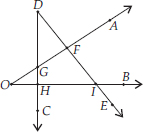
Here, two angles are ∠AOB and ∠CDE and four points F, G, H and I are common.
(E) 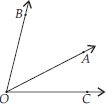
Here, two angles are ∠AOB and ∠AOC and ray OA is common.
Draw a rough sketch of a triangle ABC. Mark a point P in its interior and a point Q in its exterior. Is the point A in its exterior or in its interior?
SOLUTION:We have,
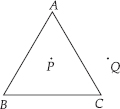
A is neither in the interior nor in the exterior of the triangle ABC. It is a vertex.
(A) Identify three triangles in the figure.
(B) Write the names of seven angles.
(C) Write the names of six line segments.
(D) Which two triangles have ∠B as common?
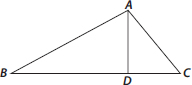
(A) The three triangles are ΔABC, ΔABD, ΔADC
(B) Seven angles are ∠ADB, ∠ADC, ∠ABD, ∠ACD, ∠BAD, ∠CAD, ∠BAC
(C) Six line segments are 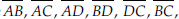
(D) Two triangles having ∠B as common are ΔABC, ΔABD
Draw a rough sketch of a quadrilateral PQRS. Draw its diagonals. Name them. Is the meeting point of the diagonals in the interior or exterior of the quadrilateral?
SOLUTION: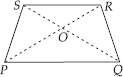
Diagonal PR and diagonal SQ meet at point O, which is in the interior of the quadrilateral PQRS.
Draw a rough sketch of a quadrilateral KLMN. State,
(A) two pairs of opposite sides,
(B) two pairs of opposite angles,
(C) two pairs of adjacent sides,
(D) two pairs of adjacent angles.
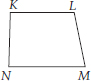
(A) Two pairs of opposite sides :
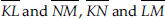
(B) Two pairs of opposite angles :
∠K and ∠M, ∠L and ∠N
(C) Two pairs of adjacent sides :
(D) Two pairs of adjacent angles :
∠K and ∠N, ∠L and ∠M
Investigate :
Use strips and fasteners to make a triangle and a quadrilateral.
Try to push inward at any one vertex of the triangle. Do the same to the quadrilateral.
Is the triangle distorted? Is the quadrilateral distorted? Is the triangle rigid?
Why is it that structures like electric towers make use of triangular shapes and not quadrilaterals?
No, the triangle is not distorted but the quadrilateral is distorted and also the triangle is rigid.
Structures like electric towers make use of triangular shape so that they could not be distorted and they could be rigid.
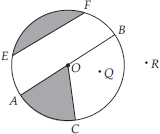
From the figure, identify :
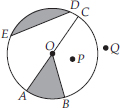
(A) the centre of circle
(B) three radii
(C) a diameter
(D) a chord
(E) two points in the interior
(F) a point in the exterior
(G) a sector
(H) a segment
(A) O is the centre of circle.
(B) Three radii : 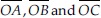
(C) A diameter : 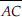
(D) A chord : 
(E) Two interior points : O and P
(F) Exterior point : Q
(G) A sector : OAB (shaded part)
(H) A segment : ED (shaded part)
(A) Is every diameter of a circle also a chord?
(B) Is every chord of a circle also a diameter?
(A) Yes, every diameter of a circle is also a chord. It is the largest chord of a circle.
(B) No, every chord of a circle is not a diameter.
Draw any circle and mark
(A) its centre
(B) a radius
(C) a diameter
(D) a sector
(E) a segment
(F) a point in its interior
(G) a point in its exterior
(H) an arc
(A) O is the centre of the circle.
(B) 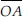 is the radius.
is the radius.
(C) 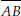 is the diameter.
is the diameter.
(D) OAC is the sector. (shaded part)
(E) EF is the segment. (shaded part)
(F) Q is a point in its interior.
(G) R is a point in its exterior.
(H) 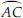 is an arc.
is an arc.
Say true or false :
(A) Two diameters of a circle will necessarily intersect.
(B) The centre of a circle is always in its interior.
(A) True
(B) True